RDWATCH: Revolutionizing Geospatial Data Analysis and AI Development
As the demand for analyzing vast amounts of geospatial data continues to grow, artificial intelligence (AI) plays a critical role in accelerating this process. Developing AI capabilities requires tools to visualize and validate results, as well as to create annotations that further improve AI models. RDWATCH is one of the latest technological developments in this area—an advanced cloud-ready system designed to streamline machine learning workflows for monitoring, annotating, and visualizing geospatial and georeferenced data.
At its core, RDWATCH is a web-based platform that provides access to a wide range of remote sensing imagery and AI-generated outputs. It assists analysts, annotators, and developers in detecting and analyzing global-scale changes by offering intuitive tools for examining data within a geospatial context.
What Sets RDWATCH Apart?
RDWATCH’s user interface is designed to enhance the user experience across a variety of tasks:
- Analyze: Closely examine model outputs—such as geospatial polygons with metadata—to detect changes over time.
- Annotate: Label data manually or with AI assistance within a geospatial context, helping to improve the accuracy of AI models.
- Refine Development: Compare AI outputs with ground truth data, identify areas where models fall short, and work to improve them.
One of the key features of RDWATCH is its ability to animate large volumes of geospatial data for any selected geospatial context, whether it’s a large region or a small area, aiding in the visualization of change detection. The ability to render and annotate time-varying model outputs and satellite images as change occurs over time sets it apart from tools that can only focus on one instant in time. This capability is made possible through the selection of appropriate server and client-side technologies that enable RDWATCH to generate dynamic vector and raster tiles on the fly and render them rapidly in a web browser.
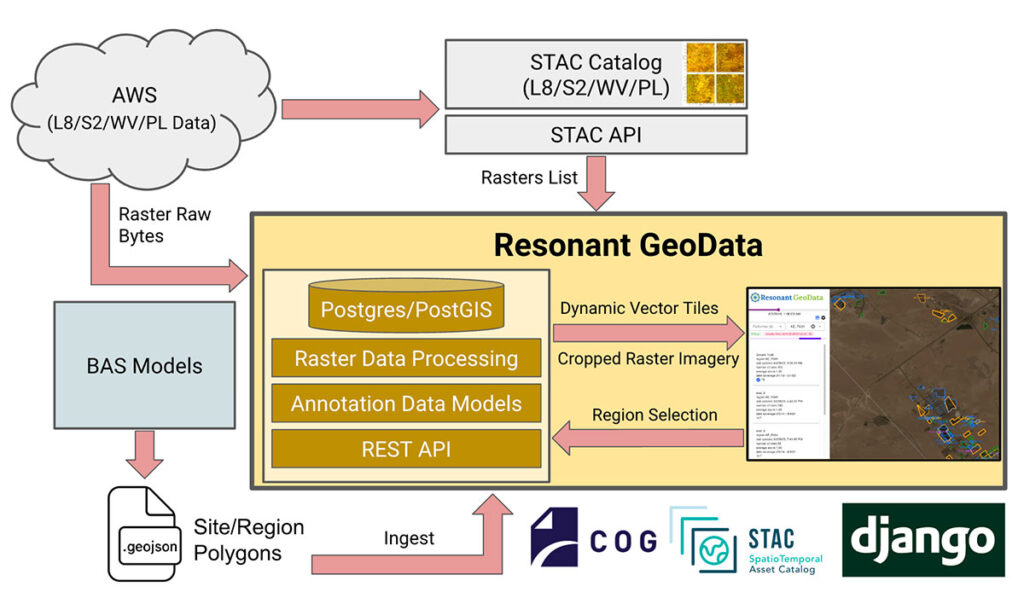
Built on top of Kitware’s Resonant GeoData platform, RDWATCH leverages open source technologies as well as emerging open standards like Spatio-Temporal Asset Catalogs (STAC). Its modular design allows it to support multiple databases and user interfaces. The data schema and interface enable RDWATCH to consume outputs from a variety of AI models, including those from Kitware’s GeoWatch system—an open source research and production environment for image and video segmentation and detection with geospatial awareness.
Key Features and Technology
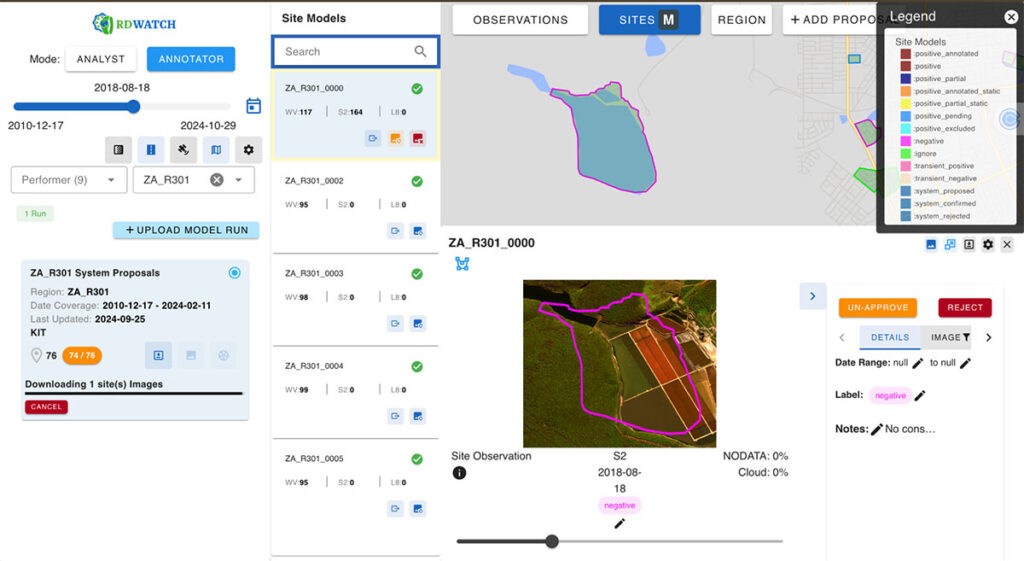
One of the standout technical features of RDWATCH is its scalable and modular architecture, which allows users to create customized interfaces for different workflows. For example, annotators can use the RDWATCH annotation interface to review, edit, and approve ground truth data. Meanwhile, the scoring view provides a detailed comparison between model outputs and ground truth, enabling users to accurately measure model performance.
Additionally, RDWATCH provides a range of interactive visualizations that enable users to watch animated changes in geospatial data over time directly within the web interface. This dynamic visualization capability is essential for anyone needing to track shifts in environmental conditions, urban development, or other phenomena that evolve across both space and time.
Under the hood, RDWATCH leverages open source technologies such as the SpatioTemporal Asset Catalog (STAC), MapLibre, Vue.js, and the Django API. These tools ensure the platform’s scalability, responsiveness, and user-friendliness. The backend is powered by AWS-managed services, providing efficient data retrieval, storage, and processing while maintaining robust security measures.
Managing Geospatial Data at Scale
RDWATCH’s strength lies in its ability to efficiently handle vast quantities of raster and vector data. It processes data in parallel, storing raster data in object storage solutions like MINIO or Amazon S3, and vector data in a PostgreSQL database. This architecture allows RDWATCH to deliver high-quality vector and raster data at multiple resolutions. Users can ingest AI model outputs in JSON or GeoJSON formats via REST APIs or a web interface. These outputs are then translated into multi-resolution dynamic vector tiles, enabling the platform to serve large volumes of time-sensitive polygons to users. Building on its robust data handling capabilities, RDWATCH utilizes tile-based streaming combined with client and server-side caching to deliver high-performance, real-time visualizations without the need for preprocessing. This approach significantly enhances the efficiency of temporal analysis, enabling users to swiftly track and interpret changes over time in geospatial data.
For annotators, RDWATCH integrates with Meta’s Segment Anything Model (SAM) (GitHub repository), providing tools to quickly create manual annotations and achieve more precise feature segmentations. This integration enhances the annotation process by leveraging SAM’s advanced capabilities, allowing for faster and more accurate data labeling.
Furthermore, RDWATCH seamlessly integrates with SpatioTemporal Asset Catalog (STAC) servers backed by cloud-hosted data storage, enhancing its data retrieval capabilities. STAC catalogs geospatial data from remote sensing imagery and provides access through a well-defined API, simplifying the data acquisition process. This integration, combined with the use of cloud-native geospatial formats, enables users to efficiently fetch data, apply processing techniques like pansharpening, and crop data to specific requirements before delivering it in real time to the client.
Another valuable feature of RDWATCH is its ability to export model outputs alongside relevant imagery for a single geospatial context (site) which is defined by the model output, or all sites, promoting collaboration across teams. Users can export time-varying annotations along with their source imagery in MP4 and GIF formats, making it easy to share and analyze geospatial changes over time.
Current and Future Applications
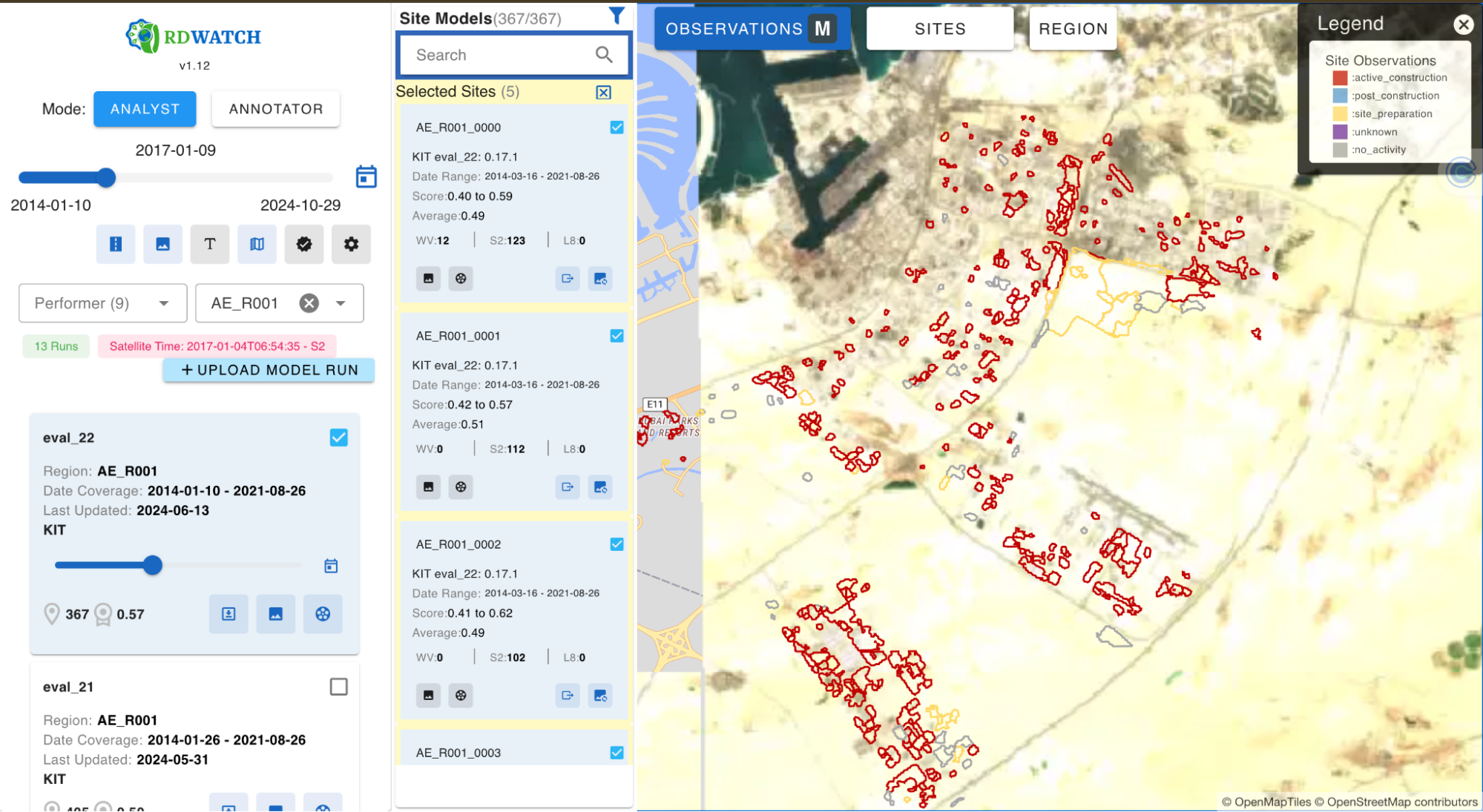
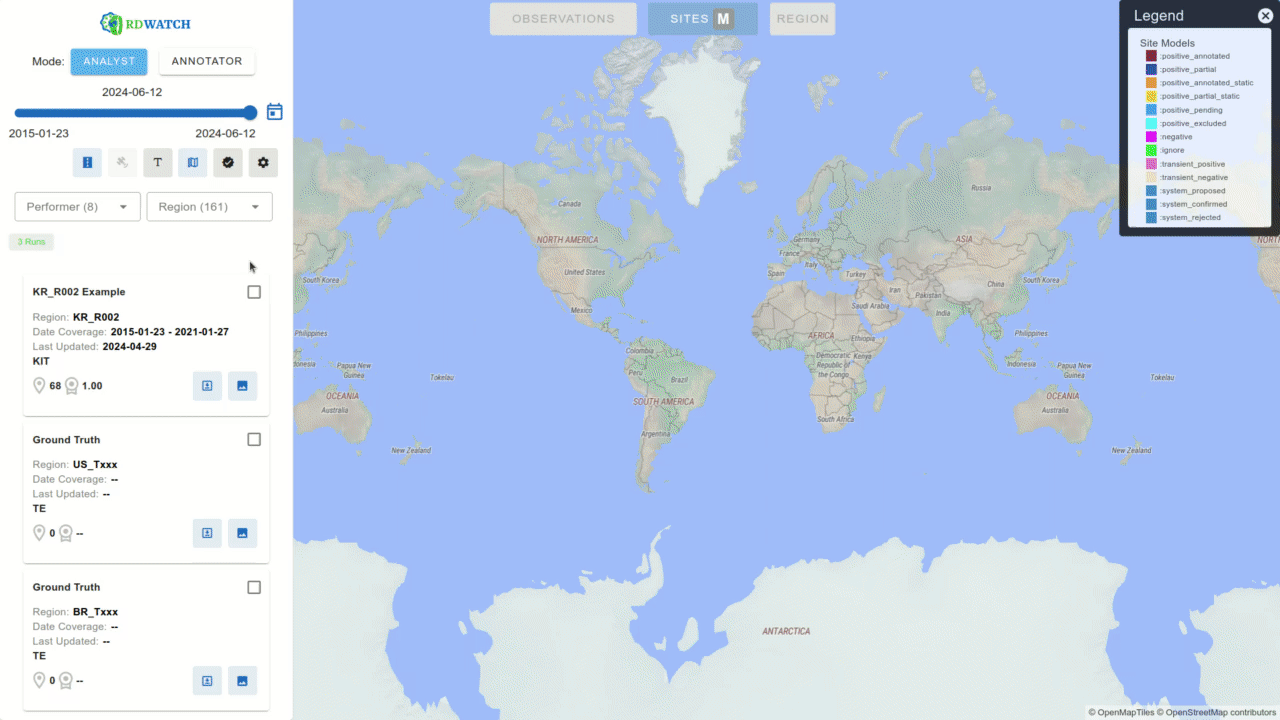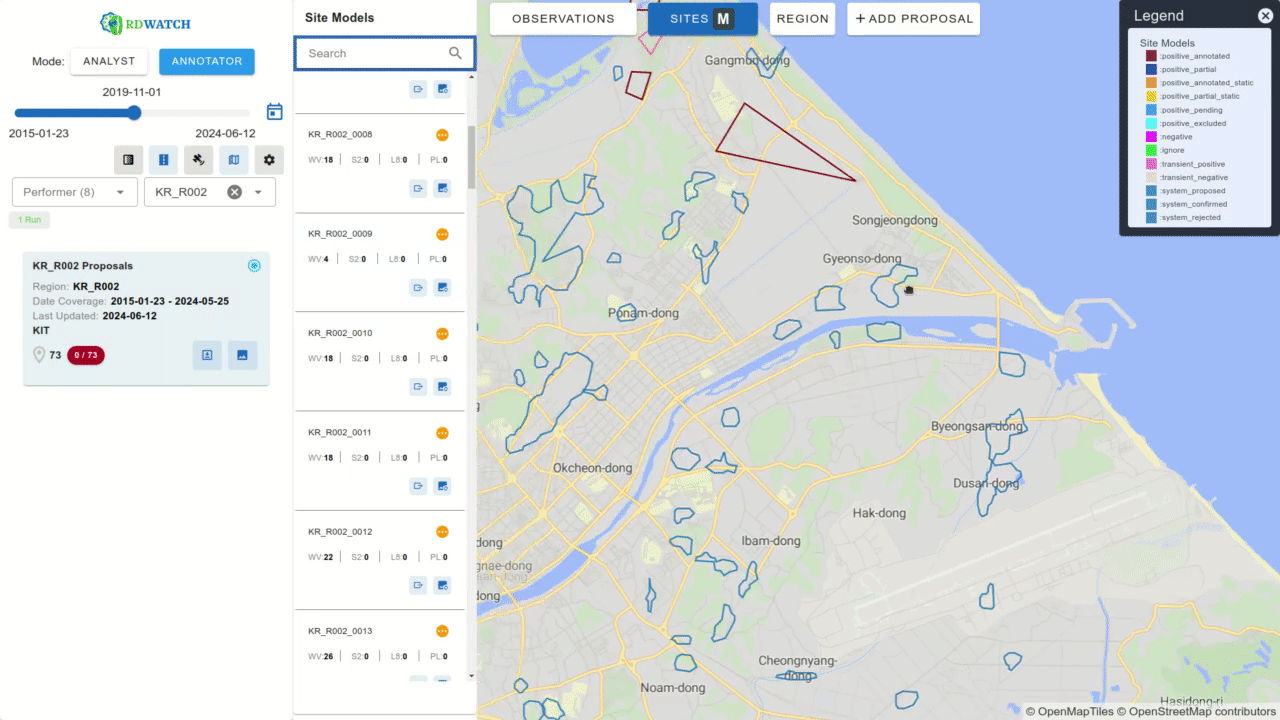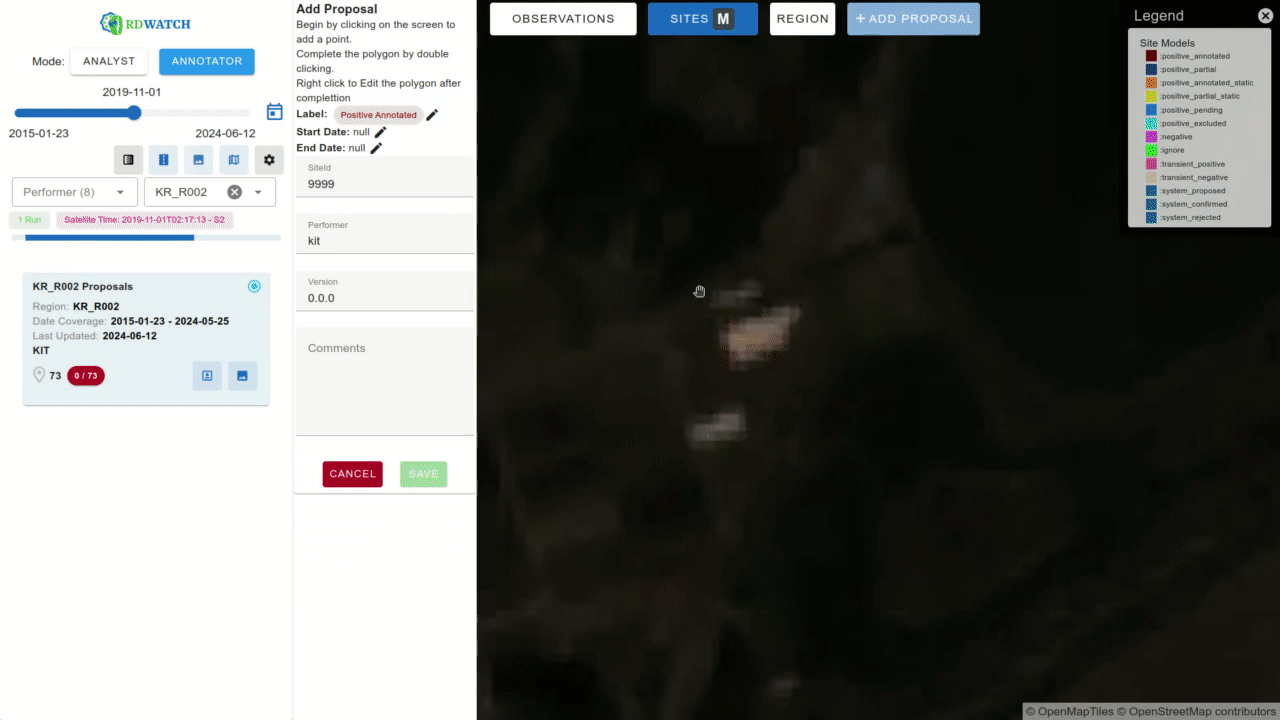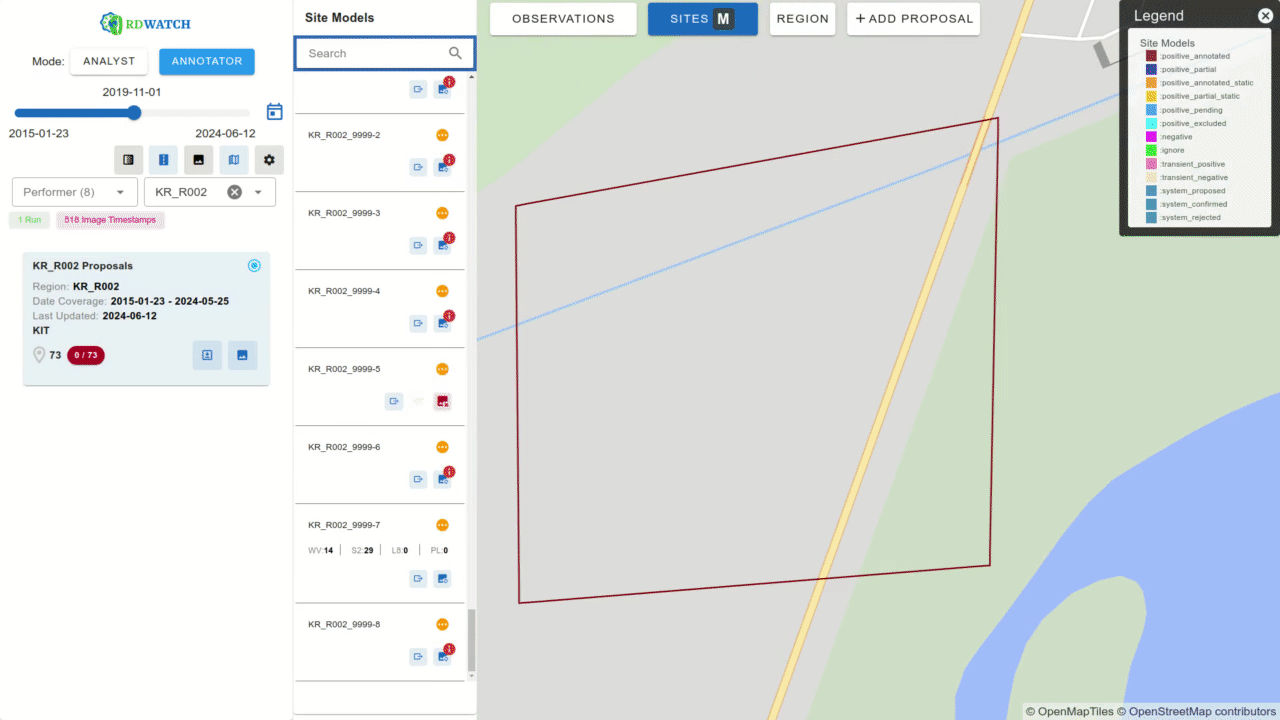
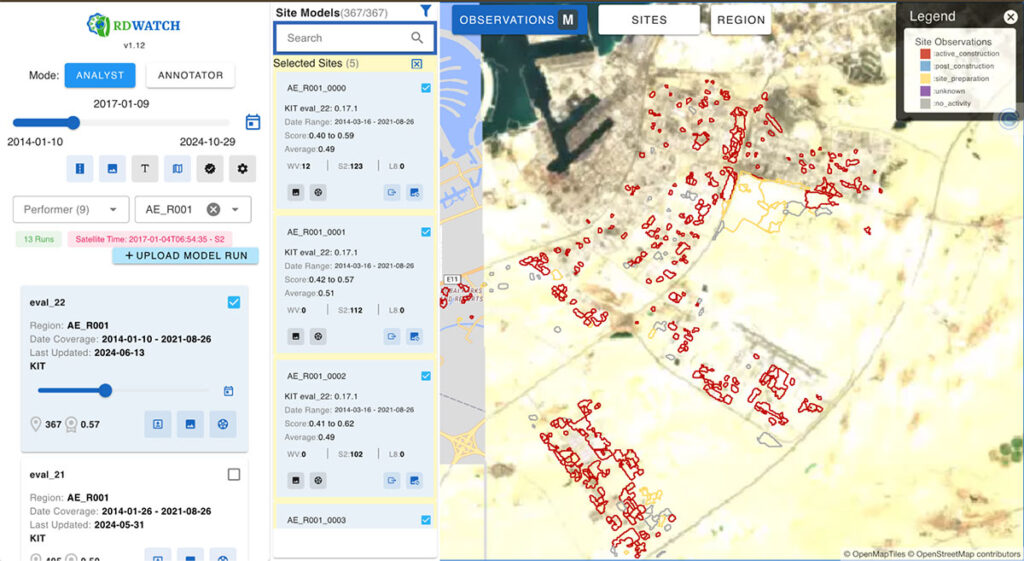
Currently, RDWATCH is being utilized to support AI model development and validation that heavily rely on remote sensing and georeferenced data which has multiple teams competing for the AI model development. The platform is leveraged to visualize model outputs that detect construction activities on a global scale. RDWATCH provides an interface to visualize model outcomes from different teams and various versions of models from the same team. Analysts can select a team, a specific model run, and a region for detailed analysis.
For each site, RDWATCH offers options to incorporate images from various satellite imagery sensors such as WorldView, Sentinel, Landsat 8, and PlanetLabs. AI-generated polygons are color-coded based on the labels produced by the models, while ground truth data is displayed with thicker outlines for distinction. Users can also apply textured patterns to ground truths for enhanced visual clarity when needed.
Another interface within RDWATCH enables annotators to create annotations or modify metadata as part of the annotation creation process or proposal acceptance workflow. This allows participants to add new sites or modify existing ones, fostering collaboration and continuous improvement of the AI models’
Beyond global-scale construction change detection, RDWATCH technology has potential applications that span from agriculture—monitoring crop health and identifying damage due to extreme weather events—to environmental monitoring, such as tracking deforestation and assessing the impacts of climate change. See Figure 4 for an example of such applications.
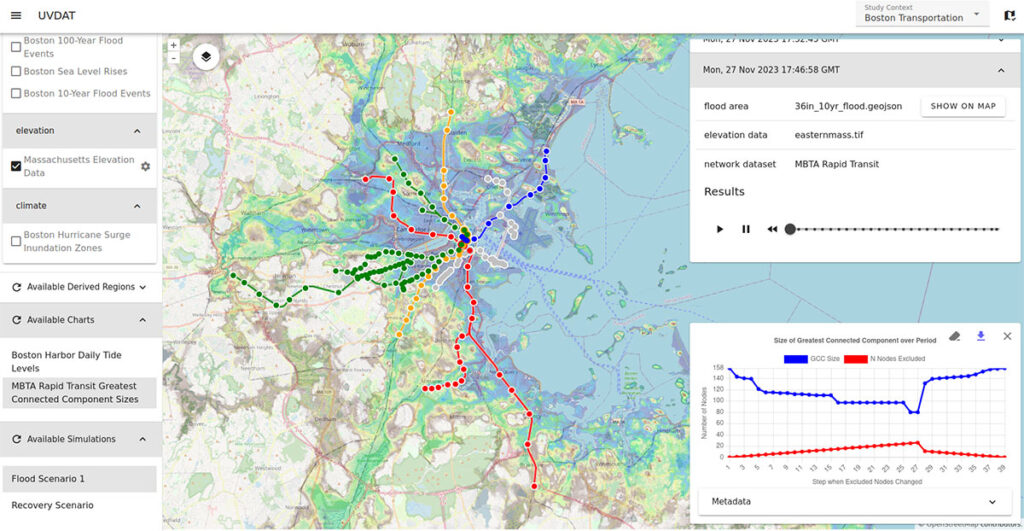
Looking forward, RDWATCH has the potential to be applied in even more diverse areas:
- Urban Planning and Infrastructure Development: Tracking changes in city landscapes and assisting in the planning of new infrastructure projects.
- Disaster Response and Recovery: Providing real-time monitoring of areas affected by natural disasters such as floods or hurricanes, enabling quicker and more efficient response strategies.
- Wildlife Conservation: Monitoring changes in natural habitats and detecting threats like deforestation or illegal land use.
These potential applications highlight RDWATCH’s versatility and its capacity to make significant contributions across various sectors that rely on geospatial data.
A Game-Changer for Geospatial Data
RDWATCH is positioned to transform how we approach AI model development and validation in the geospatial realm. By offering a scalable, user-friendly platform that seamlessly integrates AI model outputs, RDWATCH enhances workflows for a wide range of users. It empowers professionals to visualize and validate geospatial data with unprecedented efficiency and precision, leading to more accurate AI models and more informed decision-making across industries.
If you would like more information or help using RDWATCH, please contact us.
Like this article? Also check out our article on GeoWATCH, a powerful tool designed to train, predict, and evaluate AI models on complex heterogeneous sequences of imagery.
Acknowledgement
The development of RDWATCH has been primarily funded by the IARPA SMART program. This research is based upon work supported in part by the Office of the Director of National Intelligence (ODNI), Intelligence Advanced Research Projects Activity (IARPA), via 2021-201100005. The views and conclusions contained herein are those of the authors and should not be interpreted as necessarily representing the official policies, either expressed or implied, of ODNI, IARPA, or the U.S. Government. The U.S. Government is authorized to reproduce and distribute reprints for governmental purposes notwithstanding any copyright annotation therein.
Additionally, Resonant GeoData, which serves as a foundational component of RDWATCH, was developed under the Department of Defense (DoD) Small Business Innovation Research (SBIR) program. We extend our sincere gratitude to these organizations for their support and contributions to advancing geospatial data analysis technologies.