Kitware Funds Project to Aid Critical Care Physicians Treating Multiple COVID-19 Patients with a Shared Ventilator

Enhancements to Pulse Open Source Software Platform Will Help Predict Treatment Outcome
Clifton Park, N.Y. (April 2, 2020) – Kitware Inc., a leader in medical computing research and development, has launched and is fully funding a project that will help critical care physicians predict the risks associated with connecting multiple patients to a shared ventilator. As the need for ventilators increases across the country due to the rapidly accelerating COVID-19 pandemic, physicians are forced to experiment with ventilator splitting in order to try and save as many lives as possible. With this new project led by Kitware, physicians will be able to conduct these experiments via simulations first, reducing the risk to COVID-19 patients.
Numerous health care organizations, including The Society of Critical Care Medicine, American Association for Respiratory Care, and American Society of Anesthesiologists, have raised concerns over ventilator splitting due to limitations with current equipment and the lack of published knowledge on how to do so safely. Kitware’s Medical Computing Team is enhancing its open source human physiology simulator, the Pulse Physiology Engine, to contribute to finding a solution to this critical issue. The Pulse Physiology Engine is a whole-body computational physiology engine that simulates a body’s response to trauma and treatment, including the need for and effects of assisted breathing.
Due to its highly impactful nature, participation in this project has increased rapidly. Kitware is part of a working group with members from Geisinger Health, Bucknell University, Harvard University, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, Massachusetts General Hospital, and the University of Pennsylvania to deliver a platform for conducting clinical simulations under a variety of conditions. “Our updated Pulse Physiology Platform architecture and models will allow for community-wide rapid prototyping of multiplex ventilation,” said Jeffrey Webb, research and development engineer at Kitware. “Our initial in silico virtual simulation will provide quantitative data to help determine the efficacy of connecting multiple patients with different lung properties to one ventilator.”
Not only do Pulse’s simulation capabilities allow for more efficient research at a time when results are needed urgently, but it also allows for the most necessary research to be conducted via simulation, thereby keeping patients safely out of the experimental process. As Dr. Rachel Clipp, a technical leader for Kitware’s Medical Computing Team, explains, “Pulse gives us the ability to test scenarios and inform treatment protocols, including how to determine which patients to couple on one ventilator, without exposing the patients to the additional risks inherent in experimentation.”
Phase 1 of this project is expected to take only two weeks, with results immediately being published so that critical care physicians can have access and apply it to patient care right away. “Part of Kitware’s mission is to make a positive impact on the world, so it was an easy decision for the company to donate our time and resources to find a solution to this problem as quickly as possible. And we will be releasing the open source code so anyone can use it in their own clinical applications or further research,” says Dr. Clipp. “We are all proud to be a part of this research that will hopefully save many lives.”
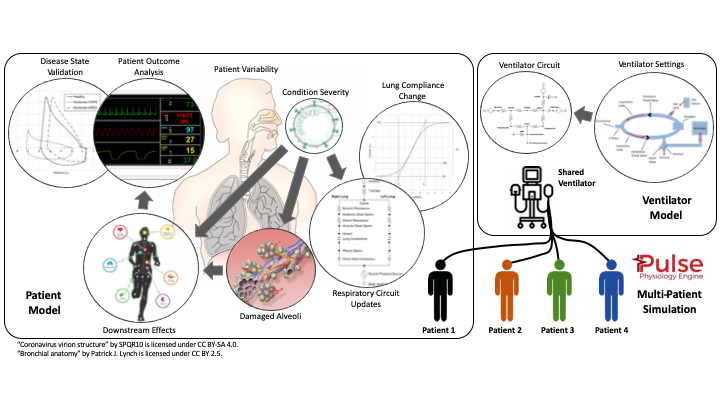
Kitware proposes a rapid simulation prototype testing the feasibility of multiplex ventilation. They plan to extend the current ventilator models for this specific application and update the software architecture to allow multiple patients to be coupled with a single ventilator.
Learn more about Kitware’s Pulse Physiology Engine and get important updates on this project by visiting https://pulse.kitware.com/.
About Kitware Inc.
Headquartered in Clifton Park, New York, Kitware Inc. has focused on advancing the frontiers of understanding by developing innovative open source software platforms and integrating them into research, processes, and products since its founding in 1998. With a wide range of capabilities, Kitware powers computer vision, data and analytics, scientific computing, medical computing, and software process implementation/management. Kitware provides expertise in these areas through customization services, support, collaborative research and development, training, and books. For additional information on Kitware, please visit kitware.com.