2024 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium
July 7-12, 2024 at the Megaron Athens International Conference Center in Athens, Greece
The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS) brings together over 2,500 scientists and professionals from the Remote Sensing field worldwide. The symposium covers a wide range of geoscience and remote sensing topics from AI and Big Data, SAR Imaging and Processing, Data Analysis, Cryosphere/Land/Atmospheres/Oceans Applications, Sensors, Mission, Instruments, and Calibration. This year’s theme is “Acting for Sustainability and Resilience,” which mirrors Kitware’s aim of creating cutting-edge solutions that make the world a better place through open science and innovation.
Kitware has a history of participating at IGARSS as a leader in the processing of satellite imagery, including two papers in the main conference this year. Kitware’s Computer Vision Team creates cutting-edge algorithms and software for automated image and video analysis, with more than two centuries of combined experience across our team in AI/ML and computer vision R&D. Our solutions have made a positive impact on government agencies, commercial organizations, and academic institutions worldwide. To learn more about our geospatial AI capabilities and how they can help you solve difficult research problems, schedule a meeting with our team.
Kitware’s Activities and Involvement at IGARSS 2024
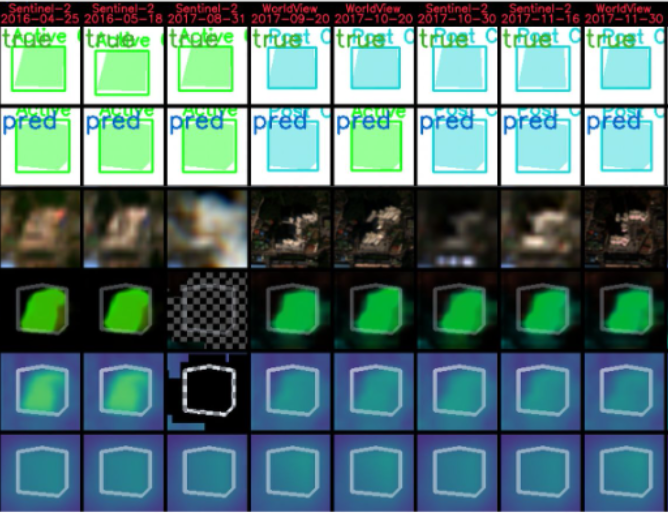
GeoWATCH For Detecting Heavy Construction In Heterogeneous Time Series Of Satellite Images
Authors: Jon Crall, Ph.D., Connor Greenwell, Ph.D., David Joy, Matthew Leotta, Ph.D., Aashish Chaudhary, Anthony Hoogs, Ph.D.

Learning from multiple sensors is challenging due to spatio-temporal misalignment and differences in resolution and captured spectra. To that end, we introduce GeoWATCH, a flexible framework for training models on long sequences of satellite images sourced from multiple sensor platforms, which is designed to handle image classification, change detection, activity recognition, object detection, or object tracking tasks. Our system includes a novel partial weight loading mechanism based on sub-graph isomorphism which allows for continually training and modifying a network over many training cycles. This has allowed us to train a lineage of models over a long period of time, applied to the problem of detecting construction of new buildings in multispectral satellite imagery collected over months or years. We have observed improved performance as we adjust configurations while maintaining a core backbone.
Building Damage Assessment From Satellite Imagery
Authors: Dennis Melamed, Cameron Johnson, Isaac D. Gerg, Ph.D., Chen Zhao, Rusty Blue, Ph.D, Philip Morrone, Anthony Hoogs, Ph.D., Brian Clipp, Ph.D.
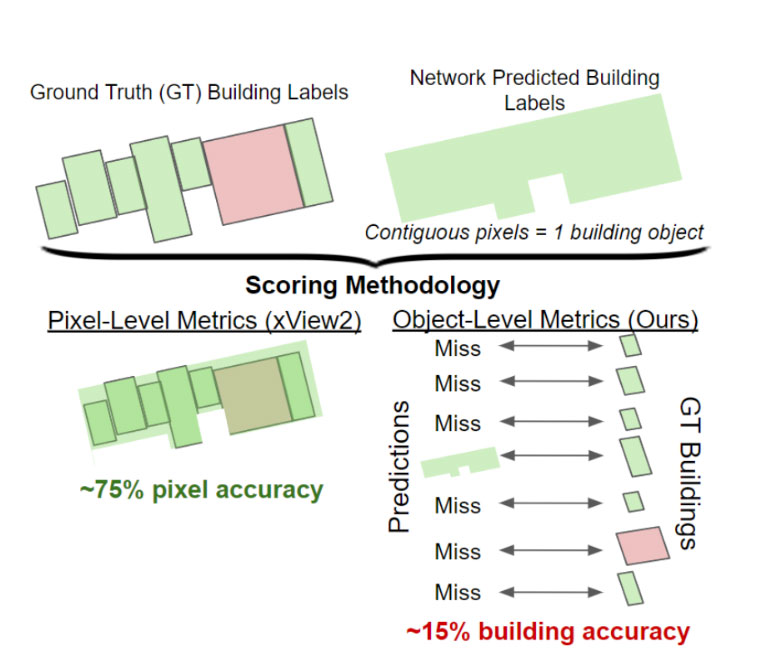
We identify a bias in a commonly used dataset for building damage detection, xBD, evaluate its effects on existing deep learning models, and devise mitigation strategies to overcome it. We find that the data contains significantly more groups of damaged buildings than individual, isolated ones. Consequently, deep learning models trained on this data tend to rely heavily on surrounding context rather than individual building damage. Specifically, the dataset includes extraneous damage surrounding buildings such as debris, fallen trees, and other damaged buildings which results in deep neural networks overfitting to these features. We analyze the top-5 solutions of the xView2 challenge, which focuses on building damage classification using the xBD dataset of satellite imagery. Our experiments reveal that these models struggle to accurately identify isolated damaged buildings, potentially causing oversights in critical disaster scenarios and delaying humanitarian aid. Finally, we devise a new augmentation strategy to reduce this bias in disaster datasets and show it improves real-world outcomes.
Kitware is Hiring!
Or join our team to enjoy numerous benefits, including support to publish your novel work, attending national and international conferences (like IGARSS!), and more. See all our benefits by visiting kitware.com/careers.
About Kitware’s Computer Vision Team
Kitware is a leader in AI/ML and computer vision. We use AI/ML to dramatically improve object detection and tracking, object recognition, scene understanding, and content-based retrieval. Our technical areas of focus include: Generative, multimodal models; Deep learning; Dataset collection and annotation; Interactive do-it-yourself AI; Explainable and ethical AI; Object detection, recognition and tracking; Complex activity, event, and threat detection; Cyber-physical systems; Image and video forensics; 3D reconstruction, point clouds, and odometry; Super resolution and enhancement; and Scene understanding. We also continuously explore and participate in other research and development areas for our customers as needed.
Kitware’s Computer Vision Team recognizes the value of leveraging our advanced computer vision and deep learning capabilities to support academia, industry, and the DoD and intelligence communities. We work with various government agencies, such as the Defense Advanced Research Project Agency (DARPA), Air Force Research Laboratory (AFRL), the Office of Naval Research (ONR), Intelligence Advanced Research Projects Activity (IARPA), and the U.S. Air Force. We also partner with many academic institutions, such as the University of California at Berkeley, Columbia, Notre Dame, the University of Pennsylvania, Rutgers, the University of Maryland at College Park, and the University of Illinois, on government contracts.
To learn more about Kitware’s computer vision work, check out our website or contact our team. We look forward to engaging with the IGARSS community and sharing information about Kitware’s ongoing research and development in AI/ML and computer vision as it relates to the latest in imaging.